We use numerical tools like finite elements and phase field methods to predict the behavior of materials from atoms to structures and solve multi-physics problems including, mechanical response, thermal transport, phase transformations, fracture, and chemical reactions. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ECYqyFspKVI
Our group is part of the following centers at Purdue University:
CHIRP: Center for heterogeneous integration research in packaging.
PERC: Purdue Energetics Research Center
Research
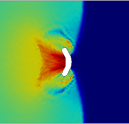
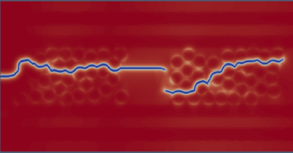
Shock to Detonation Transition: Shock to detonation transition (SDT) in energetic matrials (EM) is a process that spans multiple time and spatial scales, as well as multiple physical phenomena involving changes in chemical and mechanical properties. Deep learning models are used bridge the gap between atomistic-scale phenomena and the continuum-scale behavior of the material. The videos bellow shows the pressure of the final reaction products and the shock front propagation on a 500 micron sample of a polymer-bonded explosive (PBX) during SDT, impacted at a velocity of 1700 m/s (top), and the total mixture pressure during SDT on a 2D sample (bottom). This work is done in collaboration with: Aidan Pantoya, Chunyu Li, and Alejandro Strachan from Strachan’s Group from Materials Science and Engineering at Purdue.
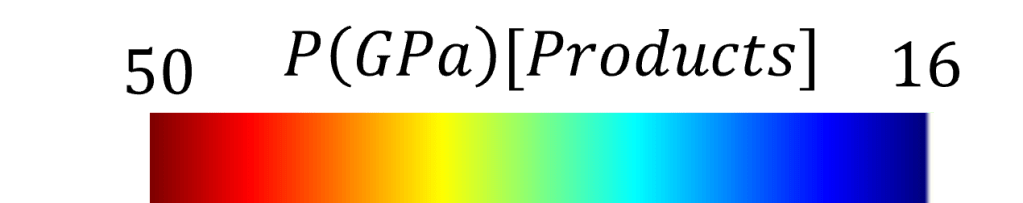
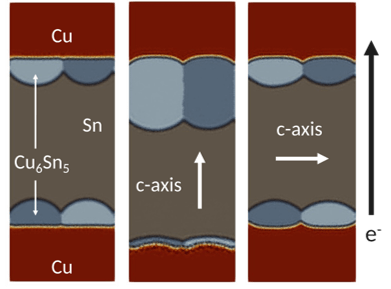
Recrystallization in Solder Joints: Sn-based solder bumps are widely used to connect different components of theinterconnects. At the Sn-Cu interface, intermetallic compounds (IMCs) are formed, which expand up to 45% andproduce large local stresses in the solder joint. The resulting local stresses trigger stress-assisted nucleation ofSn and add new grain-boundary networks in the solder microstructure, degrading the reliability. The misorientationmaps below show the location of the formation of new grains due to the IMC (in grey) volumetric expansion.



High-velocity impact: High-velocity particle impact is important for advancements in the design of supersonic vehicles, defense and ballistics, and advanced manufacturing. Our study focuses on the response of polycrystalline metals and investigates the influence of crystal orientation and grain size during the high strain rate impact of polycrystalline particles against substrates.
Corrosion-induced fracture:
Copper wire bonding on Aluminum pads is susceptible to corrosion. The volumetric expansion due to corrosion nucleates cracks at the intermetallic compound Cu9Al4/Cu interface, and these cracks eventually lead to the failure of the Cu-Al interconnects in microelectronics. The video below shows the evolution of the corrosion (red) and the crack surface (grey).
Kai-chieh Chiang and Marisol Koslowski, Corrosion-induced fracture of Cu–Al microelectronics interconnects, Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 32, 045004, 2024.
Nanocrystalline materials: Grain boundaries and interfaces play a prominent role in the deformation behavior of polycrystals rendering superior mechanical properties, including high strength and hardening. Our dislocation dynamics simulations help to understand these mechanisms to accelerate the development of materials with improved mechanical properties.
Lei Cao and Marisol Koslowski, Rate limited plastic deformation in nanocrystalline nickel, Journal of Applied Physics, 117, 244301, 2015.
Lei Cao, Abigail Hunter, Irene Beyerlein and Marisol Koslowski, The role of partial mediated slip during quasistatic deformation of nanocrystalline nickel, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 78 415-426, 2015.
Composite Materials: Carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites are used in airplanes, sailboats, cars, wind turbines, sport equipment, and many other structures where high strength-to-weight ratios are required. Delamination is a predominant failure mechanism these composites. Applying fracture dynamics in finite elements simulations we help to design composite materials that reduce the formation of extensive delamination zones.

Yuesong Xie and Marisol Koslowski, Numerical simulations of inter-laminar fracture in particle-toughened carbon fiber reinforced composites, 92, 62-69 Composites Part A, 2017.
Yuesong Xie, Oleksandr G Kravchenko; R. Byron Pipes and Marisol Koslowski, Phase field modeling of damage in glassy polymers, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 93, 182-197, 2016

Alloys and high entropy alloys: Alloys and high entropy alloys exhibit superior functional properties. We develop predictive models of flow, strengthening, ductility, and fatigue, to advance the design of alloys by selecting the composition required to achieve a specific purpose.
Yifei Zeng, Xiaorong Cai, and Marisol Koslowski, Stacking fault fluctuation effects on the strengthening of high entropy alloys, Acta Materialia, 164 1-11, 2019
Energetic Materials: Detonations in energetic materials can initiate from shock loading through a combination of chemical, thermal, and mechanical processes. The presence of microstructural defects like cracks, voids, grain boundaries, and interfaces are initiation sites for the formation of hot-spots that precede detonation. We incorporate these defects explicitly to predict ignition due to shock compression. The characteristic length of these defects is at submicron or micron scale. While transition to detonation occurs at millimeter scales. To ensure computational efficiency, we develop high-fidelity surrogate models informed from microscale simulations and we use them in detonation simulations.
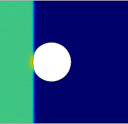
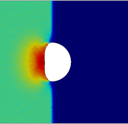

Camilo A. Duarte, Chunyu Li, Brenden W. Hamilton, A. Strachan, and Marisol Koslowski, Continuum and molecular dynamics simulations of pore collapse in shocked β- tetramethylene tetranitramine single crystals, Journal of Applied Physics, 129 015904, 2021.
Sakano, Michael; Hamed, Ahmed; Kober, Edward; Grilli, Nicolo; Hamilton, Brenden; Islam, Md Mahbubul; Koslowski, Marisol; Strachan, Alejandro, Unsupervised learning-based multiscale model of thermochemistry in RDX, Journal of Physical Chemistry, 124 44 9141-9155, 2020.
Camilo A. Duarte, Ahmed Hamed, Jonathan D. Drake, Christian J. Sorensen, Steven F. Son, Weynong W. Chen, and Marisol Koslowski, Void collapse in shocked beta-HMX single crystals: simulations and experiments, Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 45(2) 243-253, 2020.
Expounding upon previous work, we have created a finite deformation model that contains crystal plasticity, fracture, and a MieGrüneisen equation of state. We apply this model to HMX to study the influence of pore collapse and fracture of low velocity impacts to study accidental initiation of energetic materials. We study the influence of crystal orientation, impact velocity, and pore geometry on crack growth.
Periodic excitation of energetic materials: Polymer bonded explosives (PBXs) are composite materials containing energetic particles in a polymeric binder that are designed to react under a controlled stimulus. Accidental ignition followed by initiation may occur when a PBX sample is subjected to mechanical impact or vibration. We use finite element simulations to predict the damaging effect of ultrasonic vibration in PBX microstructures that can affect the ignition threshold of these composite materials.
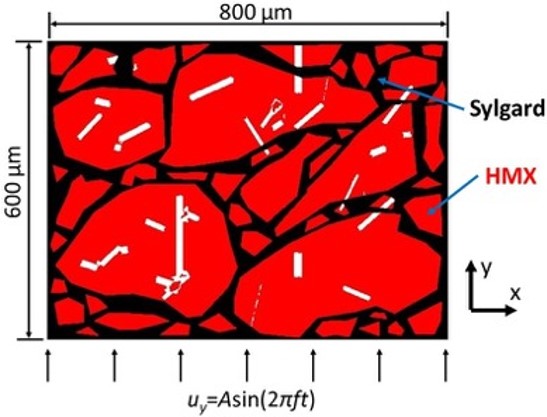
Camilo Duarte Cordon, Rachel Kohler, and Marisol Koslowski, Dynamic fracture and frictional heating due to periodic excitation in energetic materials, Journal of Applied Physics, 124 165109, 2018.
A. Dandekar and Marisol Koslowski, Effect of particle proximity and surface properties on the response of PBX under vibration, 19 110334, Computational Materials Science, 2021
Reliability of Microelectronics: Of the many lead-free solders used in the semiconductor industry, Sn-Ag-Cu (SAC) has emerged as one of the most accepted. However, the interfacial reaction of Cu with molten Sn-based solder results in the formation brittle intermetallic compounds (IMC) that accelerate the degradation of these systems. In addition, electromigration is a concern due to the miniaturization of solder joints. We develop models and simulations to predict the formation and evolution of IMCs, the nucleation of voids and the diffusion of copper due to electromigration.

X. Cai, Andew M. Pham, and Marisol Koslowski, Mechanical failure of Cu-Sn solder joints, Journal of Electronic Materials, 50:6006–6013, 2021.
Dynamic Response of Materials: We use finite elements simulations to study the response of materials under extreme conditions such as high strain rate impact and shock loading. The simulations include anisotropic crystalline plasticity, fracture, friction, and thermal response.
Nicolo Grilli and Marisol Koslowski, The effect of crystal anisotropy and plastic response on the dynamic fracture of energetic materials, Journal of Applied Physics, 126 155101, 2019.
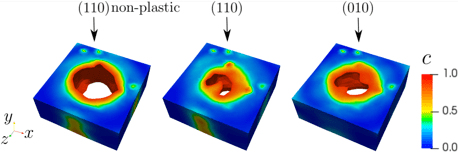
Stress relaxation in thin films: Whiskers sometimes grow from surfaces of thin films reaching lengths of several micrometers and may cause electronic system failures such as short circuits when they bridge closely-spaced circuit elements. Whiskers and hillocks appear to be responses of thin metal films to residual stresses but a single explanation to the operation of these phenomena has not been established. Finite elements simulations and experiments help to explain these mechanisms where grain orientation and recrystallization play a key role.

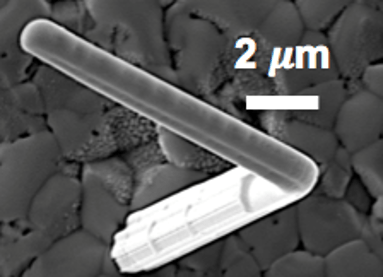
Xiaorong Cai, Carol Handwerker, John Blendell, and Marisol Koslowski, Shallow grain formation in Sn thin films, Acta Materiala, 45 1-12, 2020.
Group




Teaching
ME 581 Numerical Methods in Mechanical Engineering
https://nanohub.org/tools/purdueme581
ME 323 Mechanics of Materials https://www.purdue.edu/freeform/me323/
News
-
Recent Publication in JMPS
Recent publication on high velocity impact and recrystallization of aluminum microparticles on JMPS. This work can be accessed with the link https://authors.elsevier.com/a/1kIE157Zk992L
C. Yuan and M. Koslowski, “Grain refinement in metal microparticles subjected to high impact velocities,” Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, vol. 196, p. 106009, Mar. 2025, doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2024.106009.
-
Jack’s Publication in MSMSE
Recent publication in MSMSE on corrosion of Cu-Al interconnects.
Kai-chieh Chiang and Marisol Koslowski, Corrosion-induced fracture of Cu–Al microelectronics interconnects, Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 32, 045004, 2024.
-
TMS 2024

Congratulations to all of our presenters at TMS 2024 in Orlando Florida! Fariha, Jack, Andrew, Diane, and Chongxi presented their results to other graduate students and leading scientists in their respective fields.
Fariha’s Presentation: Anisotropic Effects in Electromigration Enhanced Intermetallic Growth in Sn Based Solders
Jack’s Presentation: Corrosion Induced Fracture of Cu/Al Interconnects in Microelectronics Packages
Andrew’s Presentation: Phase Field Simulations of Thermal Aging of Energetic Materials Thin Films
Diane’s Poster: Influence of Void Shape on the Propagation of Cracks in Energetic Materials
Chongxi’s Presentation: Local Deformation and Recrystallization during High-velocity Impact of Metallic Particles
See abstracts on TMS 2024 Website
-
A Welcome to Our New Members
We are excited to welcome several new members to the group!
Fariha Haq, who joined us in Spring 2023.
Josh Block and Alexis Byerly, who will be joining us in Fall 2023.
-
IPAM Presentation
Watch Professor Koslowski present at IPAM here!
